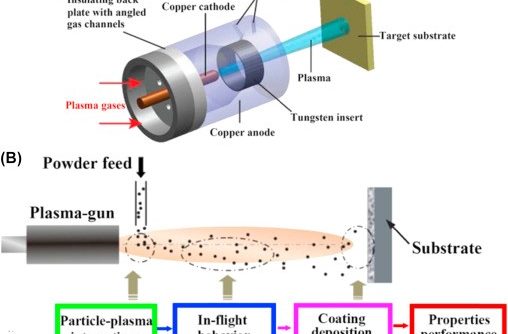
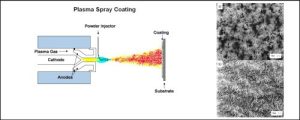
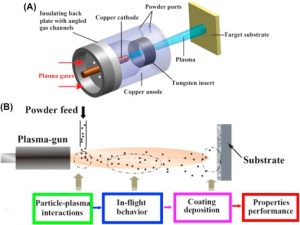
Surface coatings can give materials a host of desirable properties from corrosion resistance to water-repellence, or heat resistance to low friction and one of the best ways to apply them is by plasma spraying. The basic technique is to create a very high temperature electric arc that flash-melts the material that will form the surface and projects the ensuing ‘plasma’ as a fine spray at high velocity. When it hits the substrate it then cools almost as rapidly into a smooth, uniform surface with high adhesion. An inert carrier gas is usually present (argon, helium or nitrogen) but the material is also ionised and accelerated electromagnetically.
Plasma spray coating is the most versatile
The particles created are so fine that even delicate materials can be coated without charring or distortion. Although it is most used on metals, it is also widely applied to plastics, ceramics, glass (with appropriate preparation) and sometimes textiles. The choice of coating materials is wide so the properties that can be imparted are also many. Popular coating materials include molybdenum alumina, chrome oxide, aluminium oxide, zirconium oxide, tungsten carbide, boron carbide and even polyester composite materials, TPFE and ceramics. The process can be used on both large and small items and reliably penetrates bore holes and recesses.
Some typical applications
Plasma coating is affordable but the equipment has to be calibrated carefully so most customers rely on the support of a specialist contractor like Poeton. Each project requires a planned handling technique and careful formulation of the coating.
Very thin coatings (the range is approximately 1.4micron-1.25mm) will have minimal impact on the dimensions of precision engineered components. This quality is useful in electronic component manufacture – both on actual components and on tools such as robotic laser-engraving equipment which must be highly wear resistant. Plasma is also used to create smooth germ-resistant surfaces on medical instruments and implants (see https://www.2psmedical.com/en/plasma-coatings-on-medical-devices/).
Plasma sprays of tungsten carbide/cobalt are used to seal ring grooves and prevent wear and corrosion in gas turbines. They can also provide excellent thermal barrier coatings (and are widely used in aerospace for that purpose). Heat-proof coatings are also applied by the plasma method onto down hole tools in the oil and gas sector.
Molybdenum alloys have useful anti-galling characteristics when applied to piston rings in industrial diesel engines, and a chrome oxide ceramic mix is often applied to printing rolls used in laser engraving.




Leave a Reply